Cellular Respiration Drawing
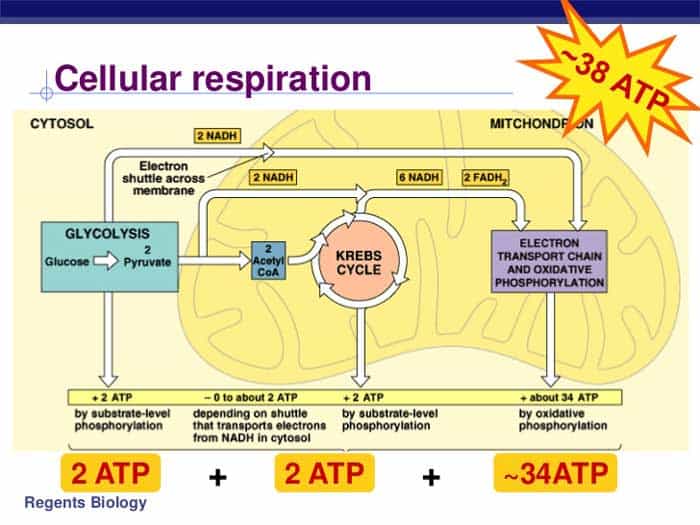
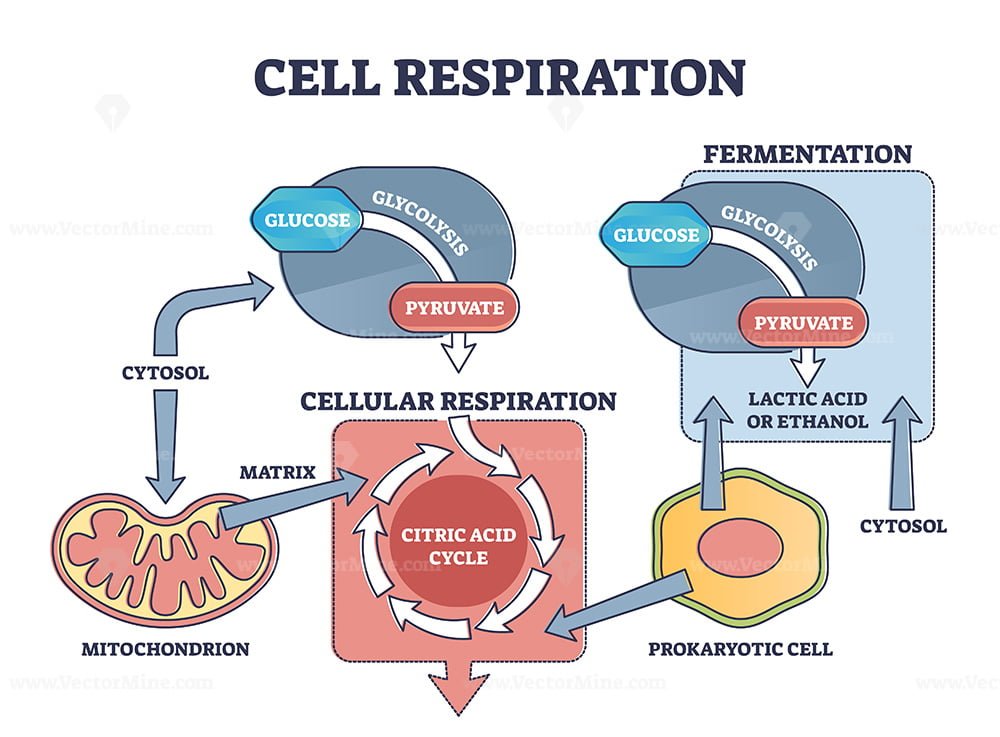
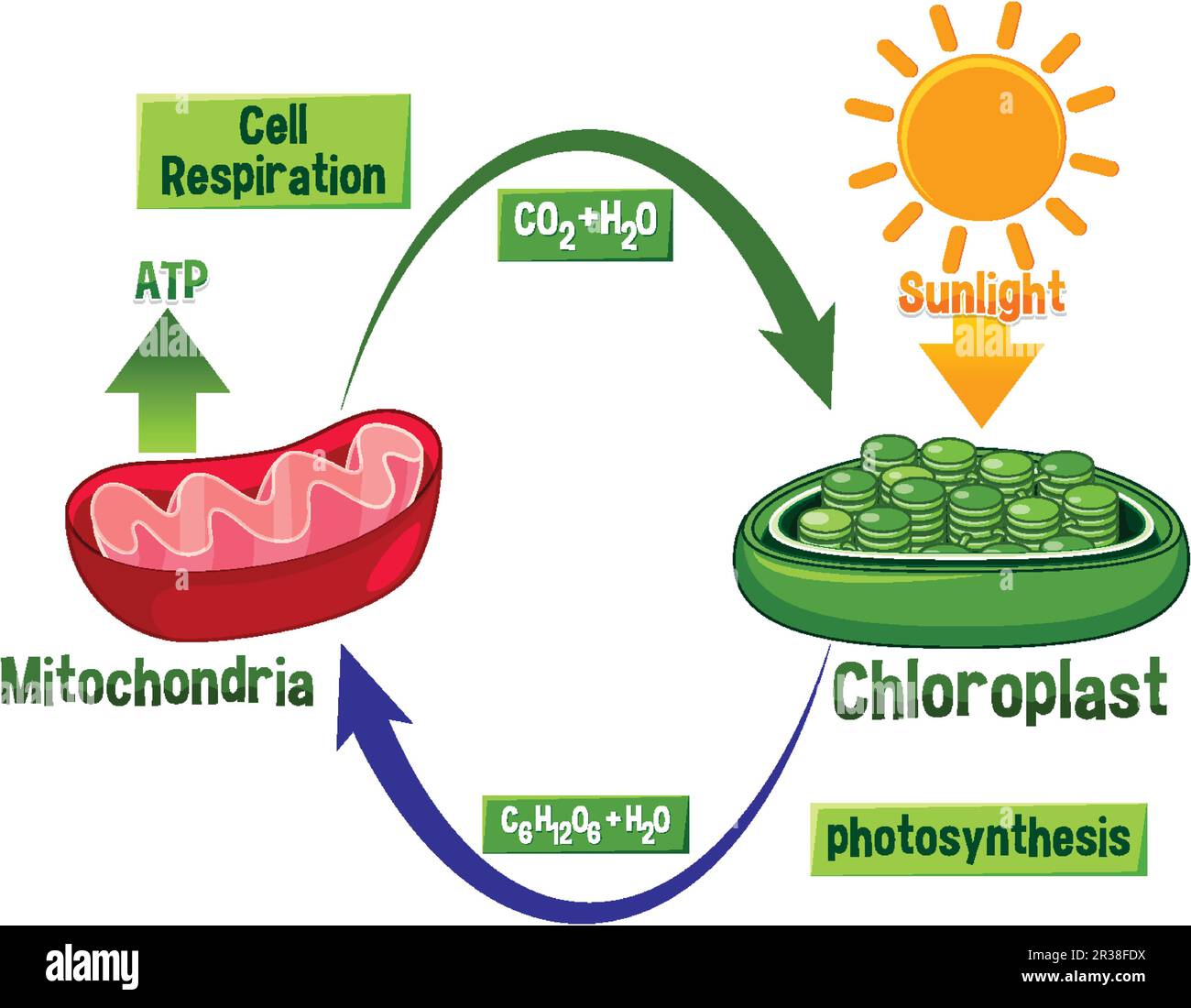
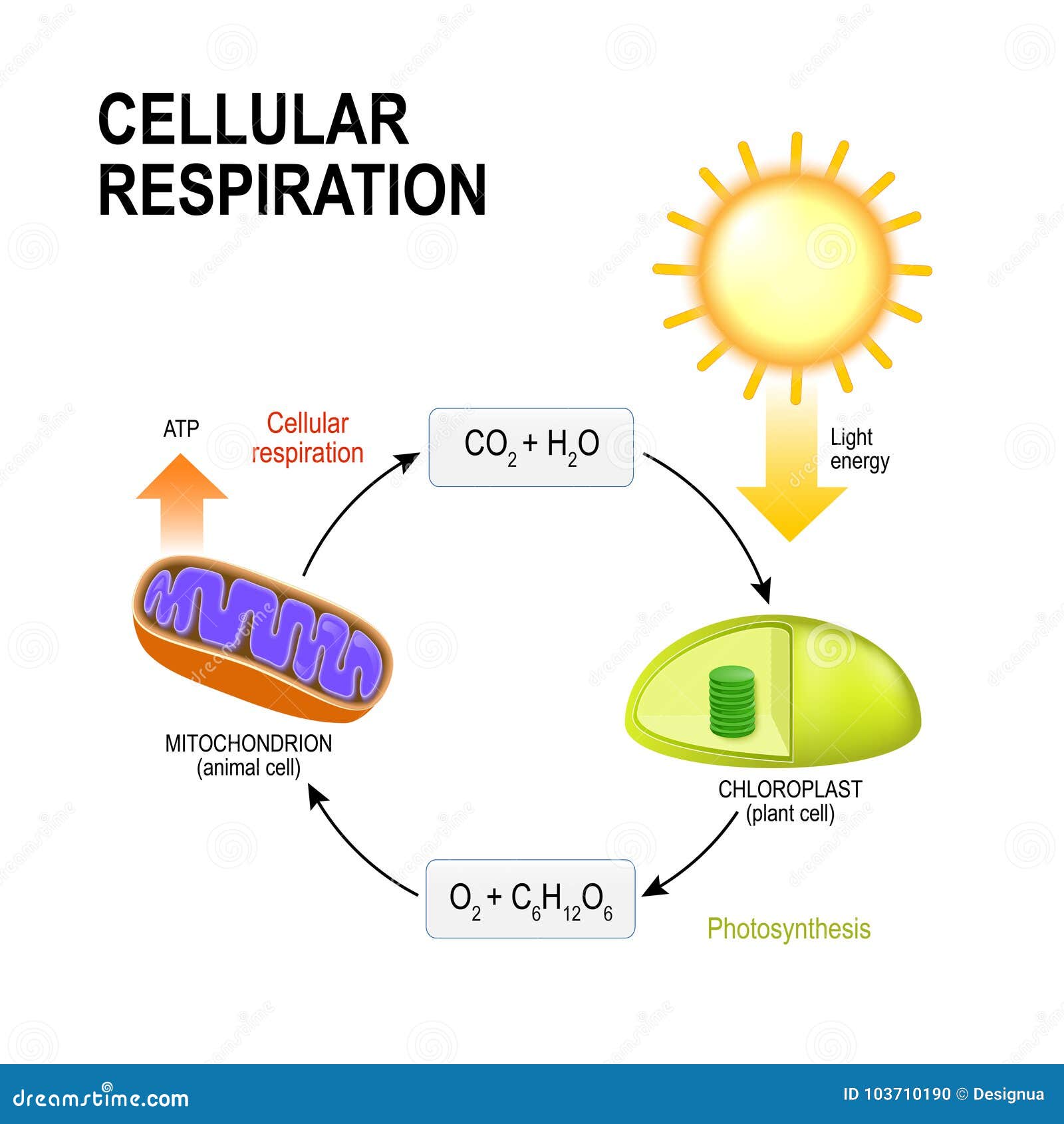
Cellular Respiration Drawing - Unit 2 water, acids, and bases. Unit 6 structure of a cell. Cellular respiration is the process by which cells derive energy from glucose. Web glucose and oxygen are inputs of cellular respiration. Web the following cellular respiration diagram illustrates the major steps of aerobic cellular respiration. Web it shows the three main stages of cellular respiration, which are glycolysis, the krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain + atp synthase. Unit 7 more about cells. Unit 4 elements of life. The following diagram of cellular respiration will give a better understanding of this process. It is the most efficient form of cellular respiration and is utilized by most eukaryotic organisms. Unit 8 membranes and transport. Unit 2 water, acids, and bases. This can be seen in the overall equation for cellular respiration: The process has three main parts: Cellular respiration is the process by which cells derive energy from glucose. Explore cellular respiration equation, types, stages & products via diagrams. Web the energy released is in the form of atp molecules that are used to carry out various functions of the cell. A word bank is provided to help them trace the flow of atp and nadh in the process as well as identifying where each step occurs. Web glycolysis takes place in the cytosol of a cell, and it can be broken down into two main phases: Web this animation shows how the enzyme complexes of the electron transport chain harvest energy from cofactor molecules to pump protons across the mitochondrial membrane and establish a chemical gradient. It is the most efficient form of cellular respiration and is utilized by most eukaryotic organisms. To create atp and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions, cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of. Add to the figure below to describe as much as you can about the processes that contribute to making. Web unit 1 intro to biology. Unit 8 membranes and transport. C6h12o6 + o2 ――> h2o + co2 + 36atp. Unit 7 more about cells. Web cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces atp. C6h12o6 + o2 ――> h2o + co2 + 36atp. Provide a concise summary of the process. There are two types of respiration: Web cellular respiration is the process by which living organisms produce energy. Most of the atp is made inside an organelle, called a mitochondrion. Web cellular respiration takes the energy stored in glucose and transfers it to atp. State what happens during glycolysis. Unit 5 energy and enzymes. To create atp and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions, cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of. Web when the glucose and oxygen reaches our cells, we have. This can be seen in the overall equation for cellular respiration: To create atp and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions, cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of. Describe the structure of a mitochondrion. Provide a concise summary of the process. Outline the steps of the krebs cycle. Web how to draw cellular respiration diagram in easy way. Unit 8 membranes and transport. Web glucose and oxygen are inputs of cellular respiration. In most multicellular organisms, cellular respiration occurs in the form of aerobic respiration. Web it shows the three main stages of cellular respiration, which are glycolysis, the krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain + atp. Web it shows the three main stages of cellular respiration, which are glycolysis, the krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain + atp synthase. Web cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces atp. Web glucose and oxygen are inputs of cellular respiration. Describe the structure of a mitochondrion. C6h12o6 + o2 ――> h2o + co2. The following diagram of cellular respiration will give a better understanding of this process. Though a sequence of specialized enzymes, the glycolysis pathway ultimately converts each glucose molecule into two pyruvate. Web the energy released is in the form of atp molecules that are used to carry out various functions of the cell. Web unit 1 intro to biology. The. There are two types of respiration: Web unit 1 intro to biology. C6h12o6 + o2 ――> h2o + co2 + 36atp. In most multicellular organisms, cellular respiration occurs in the form of aerobic respiration. Web cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces atp. The chemical reaction for cellular respiration involves glucose and oxygen as inputs, and produces carbon dioxide, water, and energy (atp) as outputs. Web the following cellular respiration diagram illustrates the major steps of aerobic cellular respiration. It is the most efficient form of cellular respiration and is utilized by most eukaryotic organisms. The following diagram of cellular respiration will give. The cellular respiration equation is as follows: Unit 8 membranes and transport. Inside your cells, cellular respiration uses oxygen plus molecules from food to provide the energy to make atp. Web cellular respiration takes the energy stored in glucose and transfers it to atp. Carbon dioxide and water are outputs. Web it shows the three main stages of cellular respiration, which are glycolysis, the krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain + atp synthase. State what happens during glycolysis. It is the most efficient form of cellular respiration and is utilized by most eukaryotic organisms. The process of cellular respiration involves the breakdown of high energy bonds, which release energy in the form of atp. The process has three main parts: To create atp and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions, cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of. Unit 2 water, acids, and bases. A word bank is provided to help them trace the flow of atp and nadh in the process as well as identifying where each step occurs. The following diagram of cellular respiration will give a better understanding of this process. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Web cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces atp.Cellular Respiration Equation, Types, Stages, Products & Diagrams
Diagram showing process cellular respiration Vector Image
How To Draw Cellular Respiration Diagram in Easy Way YouTube
Cellular Respiration Steps And Location
Cell respiration process explanation with biological stages outline
Cellular Respiration Tribuntech
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Diagram illustration Stock
Cellular Respiration. Connecting Cellular Respiration and Photos Stock
Cellular Respiration Labeled Diagram sportcarima
Cellular respiration Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
Web What Is The Purpose Of Cellular Respiration?
In Brief, Food Energy From Fats Or Starches Is Converted Into Molecules Of Glucose.
Though A Sequence Of Specialized Enzymes, The Glycolysis Pathway Ultimately Converts Each Glucose Molecule Into Two Pyruvate.
Web Glycolysis Takes Place In The Cytosol Of A Cell, And It Can Be Broken Down Into Two Main Phases:
Related Post:





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cellular_respiration-8fcc3f1ad3e54a828dabc02146ce4307.jpg)